Professional Manufacturer of Biomagnetic Beads

Optimizing H. pylori Detection with Magnetic Bead DNA Extraction
Introduction
Magnetic bead-based nucleic acid extraction is currently the mainstream and gold standard technology playing a crucial role in the molecular detection of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). Today, we will explore in detail the application, specific protocols, and future prospects of magnetic bead-based nucleic acid extraction technology in Helicobacter pylori nucleic acid testing.
1. Application: Why is the Magnetic Bead Method Particularly Suitable for H. pylori Nucleic Acid Testing?
Samples for H. pylori detection typically include gastric mucosal tissue (biopsy), stool, saliva, or dental plaque. These samples are complex in composition, containing large amounts of host cells, mucus, food debris, bile acids, and various PCR inhibitors.
Therefore, efficient and pure nucleic acid extraction is critical to ensuring the accuracy of subsequent nucleic acid tests (such as qPCR, digital PCR, and sequencing).
1.1 The magnetic bead method offers significant advantages in this context
- High Purity and Yield: Magnetic beads effectively adsorb nucleic acids and remove impurities such as proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids through multiple washing steps. They are particularly effective at eliminating PCR inhibitors in complex gastrointestinal samples, greatly enhancing detection sensitivity and specificity.
- Automation and High Throughput: The magnetic bead method is highly amenable to automation. Numerous automated nucleic acid extraction instruments are available that can process dozens or even hundreds of samples simultaneously, significantly improving efficiency, reducing human error, and meeting the demands of large-scale clinical testing and epidemiological screening.
- Safety and Simplicity: The entire process is conducted in sealed deep-well plates, minimizing aerosol contamination and reducing operators’ exposure to hazardous reagents, thereby enhancing biosafety.
- Flexibility: The method is suitable for various sample types, including gastric tissue, stool, and oral samples, with minor adjustments to the lysis buffer配方 and operating parameters.
- Standardization: Automated processes ensure high standardization, reliable results, and facilitate inter-laboratory comparisons and quality control.
2. Protocol: Magnetic Bead-Based Nucleic Acid Extraction and Detection Workflow for H. pylori
The following is a standard automated magnetic bead-based protocol for extracting H. pylori DNA (using gastric tissue or stool samples as examples):
2.1 Sample Pre-Treatment
Gastric Mucosal Tissue: Place biopsy tissue in a PBS-containing centrifuge tube and homogenize thoroughly using a tissue grinder.
Stool Sample: Suspend a small amount (e.g., 100–200 mg) of stool sample in a specific sample preservation solution or PBS buffer, vortex to mix, and centrifuge to collect the supernatant.
2.2 Nucleic Acid Extraction (Using a 96-Well Automated Extraction System)
Lysis: Take 200 μL of the processed sample supernatant and add it to a powerful lysis buffer containing proteinase K (e.g., a guanidine HCl-based denaturing salt system). Incubate at 60–70°C for 10–20 minutes to fully lyse cells and bacteria, release nucleic acids, and inactivate any potential nucleases.
Binding: Add binding buffer and magnetic bead suspension to the lysate and mix. Under the high ionic strength of the denaturing salt, DNA specifically adsorbs onto the surface of the magnetic beads. After incubating for several minutes, capture the bead-DNA complexes using a magnetic stand and discard the supernatant.
Washing:
Wash Buffer I: Typically contains high concentrations of salt and ethanol to remove proteins, lipids, and other impurities.
Wash Buffer II: Usually contains low concentrations of salt and ethanol to remove salts and residual inhibitors.
After each wash step, resuspend the beads, capture them, and discard the liquid. Repeat 2–3 times.
Drying: After completely removing the wash buffer, leave the tube open at room temperature for a few minutes or apply mild heat to allow residual ethanol to evaporate fully, avoiding interference with subsequent PCR reactions.
Elution: Add a low-salt or salt-free elution buffer (e.g., Tris-EDTA buffer or sterile water), resuspend the beads, and incubate at 55–65°C for 5–10 minutes to dissociate the DNA from the beads. Finally, capture the beads using a magnetic stand, and the resulting supernatant contains the purified H. pylori DNA template.
2.3 Nucleic Acid Detection
Add the extracted DNA template to a real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) reaction system.
Target Genes: Commonly selected highly specific conserved genes of H. pylori include:
- Urease A gene (ureA): Most commonly used, with extremely high specificity.
- 16S rRNA gene: Highly conserved, suitable for genus-level identification.
- cagA gene: A virulence gene used to distinguish high-virulence strains.
Reaction: Perform amplification in a qPCR instrument and monitor the fluorescence signal to determine results. Positive samples will show a characteristic S-shaped amplification curve.
Quality Control
Internal Control (IC): Added at the beginning of extraction to monitor the success of the entire process and avoid false negatives.
Positive and Negative Controls: Included in each experiment to ensure the effectiveness of extraction and PCR reagents.
3. Prospects and Future Directions
The prospects for magnetic bead-based nucleic acid extraction technology in H. pylori detection are vast and will develop in the following directions:
- Fully Integrated “Sample-in, Result-out” Systems: Future trends involve integrating nucleic acid extraction, amplification, and detection into a single microfluidic chip or cartridge. Users need only add the sample, and the instrument automatically completes the entire process and generates a report. This will greatly simplify operations, shorten detection time (potentially to within 1 hour), and make it highly suitable for outpatient clinics, primary care hospitals, and even home use.
- Multiplex Detection and Drug Resistance Gene Analysis: High-quality nucleic acids extracted via the magnetic bead method support multiplex qPCR testing. A single reaction can not only determine H. pylori infection but also detect multiple drug resistance genes (e.g., clarithromycin resistance mutation 23S rRNA, levofloxacin resistance mutation gyrA), integrating molecular diagnosis and drug susceptibility testing to provide direct guidance for precise clinical treatment.
- Metagenomics and Strain Typing: High-quality DNA extraction is a prerequisite for metagenomic sequencing (mNGS). The magnetic bead method can provide high-quality templates for mNGS, enabling research on H. pylori microbiota diversity, evolutionary relationships, and interactions with other microorganisms in the infection microenvironment, thereby advancing deeper mechanistic studies.
- Popularization of Non-Invasive Testing: Stool-based H. pylori DNA testing (stool antigen test, SAT) is an excellent non-invasive method. The maturation of automated magnetic bead-based extraction will make large-scale stool screening feasible, suitable for children, individuals intolerant to endoscopy, and post-treatment efficacy monitoring.
- Continuous Technological Optimization: Magnetic beads, buffer formulations, and instrument designs will continue to be optimized to achieve faster (shortening to within 20 minutes), more cost-effective (reducing per-test costs), and greener (using more environmentally friendly reagents) extraction of higher-purity nucleic acids.
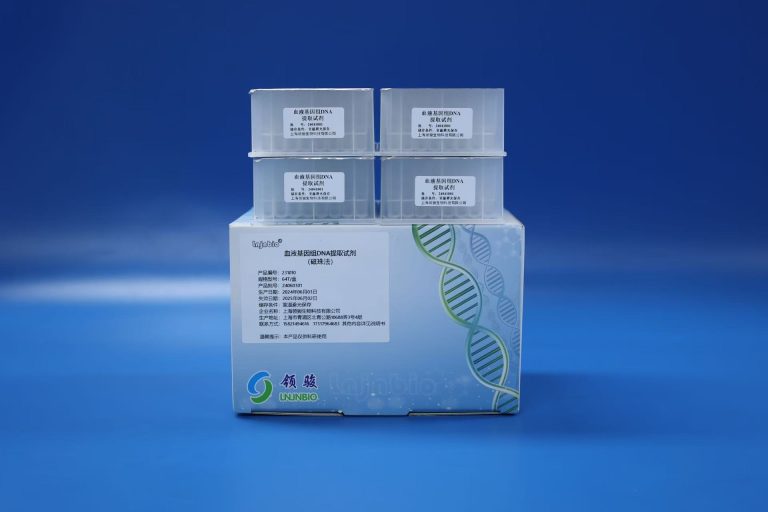
4. Product Recommendation
Shanghai Lingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. offers various models of silica-based magnetic beads widely used in pathogen disease diagnostics, particularly the 160013 magnetic beads, which are suitable for Helicobacter pylori nucleic acid extraction. The 160013 magnetic beads provide extremely high detection sensitivity, enabling early screening during infection and valuable time for disease control and prevention.
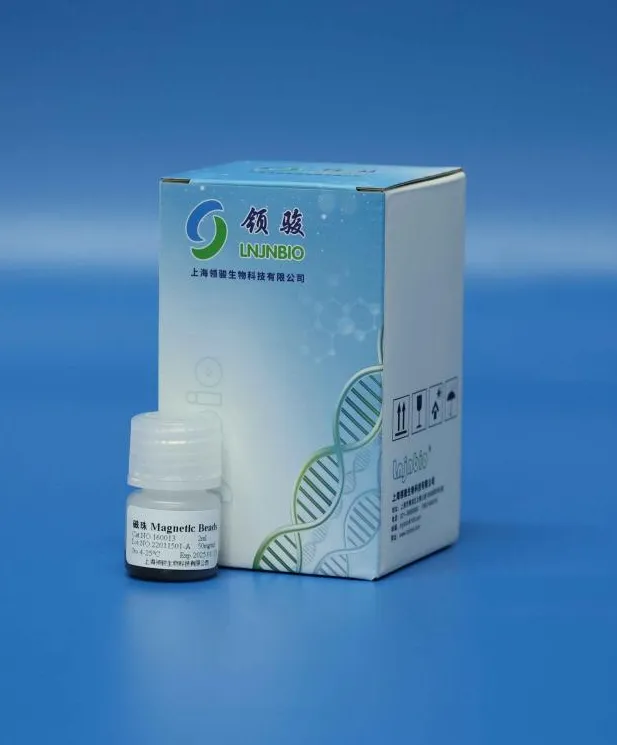
【Product Specifications】
Product Code: 160013
Solid Content: 50 mg/mL
Packaging: 2 mL / 10 mL / 50 mL / 500 mL / 1000 mL
【Product Parameters】
Active Group: Si-OH
Magnetic Bead Matrix: Silicon Dioxide
Average Particle Size: 1.2 µm
Magnetic Saturation Strength: 65 ± 5 emu/g
【Product Advantages】
High adsorption rate: Maximum recovery rate exceeding 95%.
Excellent suspension and strong magnetic properties for easy operation.
High purity and sensitivity in nucleic acid extraction.
Mature production process with excellent batch-to-batch consistency.
Conclusion
Magnetic bead-based nucleic acid extraction technology, with its advantages of automation, high throughput, high purity, and high safety, has become the gold standard method for nucleic acid preparation in Helicobacter pylori molecular diagnostics. It not only ensures the reliability of current qPCR testing but also serves as a key technological foundation for advancing rapid, precise, and non-invasive diagnosis of H. pylori infection. As molecular technologies continue to evolve and integrate, the application of magnetic bead-based methods in this field will only become more profound and widespread.
Supplier
Shanghai Lingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. was established in 2016 which is a professional manufacturer of biomagnetic materials and nucleic acid extraction reagents.
We have rich experience in nucleic acid extraction and purification, protein purification, cell separation, chemiluminescence, and other technical fields.
Our products are widely used in many fields, such as medical testing, genetic testing, university research, genetic breeding, and so on. We not only provide products but also can undertake OEM, ODM, and other needs. If you have a related need, please feel free to contact us .