Professional Manufacturer of Biomagnetic Beads

Want to Treat Industrial Wastewater More Efficiently?
Introduction
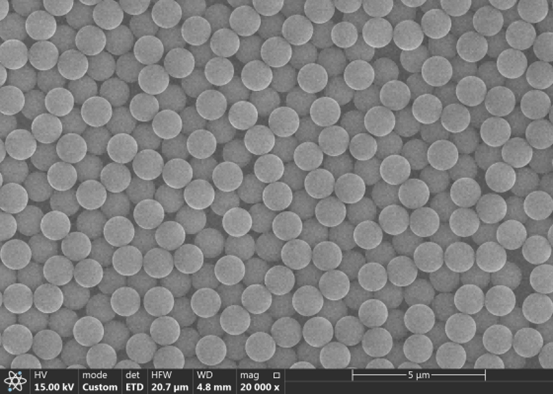
In the field of industrial wastewater treatment, silica-based magnetic microspheres have emerged as star materials for efficient purification due to their unique magnetic separation capabilities. This article provides an in-depth analysis of three typical functionalized magnetic beads – silica-based amino magnetic beads, silica-based carboxyl magnetic beads, and unmodified silica-based magnetic beads – examining their technical characteristics and application prospects.
1. Silica-Based Amino Magnetic Beads: Heavy Metal Capture Specialists
- Application Areas: Wastewater containing heavy metals from electroplating, metallurgy, mining operations
- Mechanism: Surface amino groups (-NH₂) form stable coordination bonds with heavy metal ions (Zn²⁺, Cu²⁺, Pb²⁺, etc.)
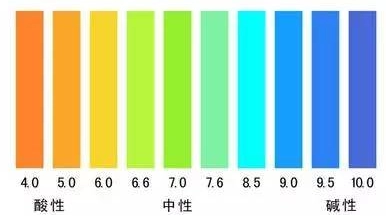
- Performance: Zinc ion adsorption capacity reaches 280-350 mg/g with >95% removal rate at pH 5-7
II. Silica-Based Carboxyl Magnetic Beads: Dye Wastewater Scavengers
- Application Areas: Printing, dyeing, textile, and pigment production wastewater
- Mechanism: Carboxyl groups (-COOH) capture cationic dyes through ion exchange and complexation
- Performance: Methylene blue adsorption capacity of 400-550 mg/g, maintaining 80% efficiency after 5 regeneration cycles
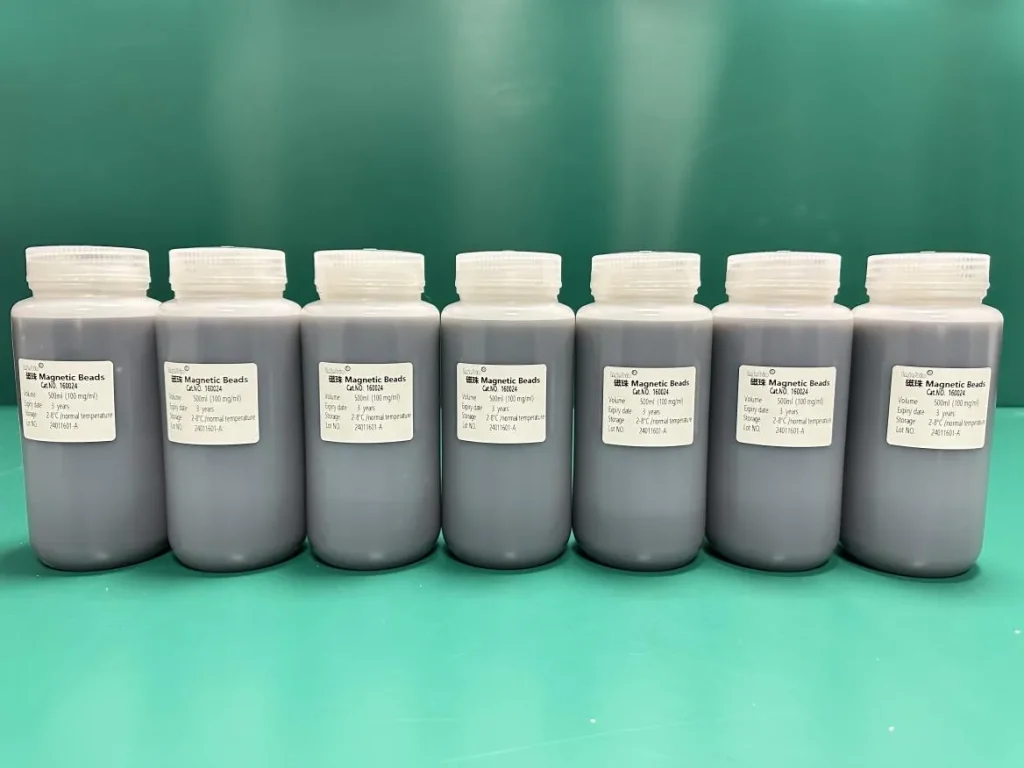

3. Unmodified Silica-Based Magnetic Beads: Biological Treatment Enhancers
- Application Areas: Municipal sewage, food processing, aquaculture wastewater with high biodegradability
- Mechanism: Silanol groups (-SiOH) promote microbial biofilm formation, enhancing biological treatment systems
- Performance: Increases activated sludge denitrification efficiency by 15-20% and improves sludge settling velocity by 30%
3.1 Technical Advantages Comparison
All three magnetic bead types exhibit superparamagnetism, enabling rapid solid-liquid separation within 30 seconds. Amino magnetic beads demonstrate selective adsorption for heavy metals, carboxyl magnetic beads show broad-spectrum adsorption capability for organic dyes, while unmodified silica-based magnetic beads excel in enhancing biological system stability.
3.2 Product Introduction
Shanghai Lingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. has developed various models of silica-based amino magnetic beads, silica-based carboxyl magnetic beads, and unmodified silica-based magnetic beads, widely applicable to industrial wastewater treatment. This technology enables efficient, selective adsorption and removal of pollutants through simple magnetic separation, achieving rapid wastewater purification and potential resource recovery.
Shanghai Lingjun’s three magnetic bead products offer the following advantages:
- High adsorption capacity: High surface group density provides abundant binding sites for bioconjugation or pollutant adsorption
- Superparamagnetism: Strong magnetic responsiveness enables rapid magnetic separation with simple, efficient operation
- Excellent stability: Superior physicochemical stability, dispersibility, and resuspension ensure batch-to-batch reproducibility
- Surface modifiability: Further functionalization can be customized according to application requirements
- Broad applicability: Versatile materials seamlessly bridging biological research and industrial wastewater treatment scenarios
Table 1: Shanghai Lingjun Silica-Based Amino Magnetic Beads Specifications
| Product Name | Product Code | Surface Group | Particle Size | Amino Content | Solid Content | Specification |
| Amino Magnetic Beads | 220031 | -NH₂ | 4 μm | ≥300 μmol/g | 200 mg/mL | 2mL, 10mL, 50mL, 500mL, 1000mL |
| Amino Magnetic Beads | 220032 | -NH₂ | 1.2 μm | ≥500 μmol/g | 50 mg/mL | 2mL, 10mL, 50mL, 500mL, 1000mL |
Table 2: Shanghai Lingjun Silica-Based Magnetic Beads Specifications
| Product Code | Product Name | Surface Group | Particle Size | Solid Content | Specification |
| 160011 | Silica Magnetic Beads | Si-OH | 800 nm | 50 mg/mL | 2mL, 10mL, 50mL, 500mL, 1000mL |
| 160013 | Silica Magnetic Beads | Si-OH | 1.2 μm | 50 mg/mL | 2mL, 10mL, 50mL, 500mL, 1000mL |
| 160024 | Silica Magnetic Beads | Si-OH | 1.4 μm | 100 mg/mL | 2mL, 10mL, 50mL, 500mL, 1000mL |
Table 3: Shanghai Lingjun Silica-Based Carboxyl Magnetic Beads Specifications
| Product Name | Product Code | Surface Group | Particle Size | Carboxyl Content | Solid Content | Specification |
| Carboxyl Magnetic Beads | 160012 | -COOH | 800 nm | ≥500 μmol/g | 50 mg/mL | 2mL, 10mL, 50mL, 500mL, 1000mL |
| Carboxyl Magnetic Beads | 160015 | -COOH | 2.0 μm | ≥400 μmol/g | 100 mg/mL | 2mL, 10mL, 50mL, 500mL, 1000mL |
4.Conclusion
With advancements in surface modification technology, functionalized magnetic beads are evolving toward intelligent and specialized applications:
• Genetic engineering modifications: Combining specific peptide chains with amino magnetic beads to enhance recognition capability for trace heavy metals like arsenic and mercury
• Composite functional design: Constructing amino-carboxyl dual-modified magnetic beads for simultaneous removal of heavy metals and organic pollutants
• Low-carbon process integration: Combining photovoltaic-driven magnetic separation systems to achieve “zero-carbon operation” in wastewater treatment
5. Summary
Functionalized magnetic beads have become core materials for advanced industrial wastewater treatment due to their precise targeting, rapid separation, and recyclable characteristics. By accurately matching pollutant characteristics with magnetic bead functions, enterprises can significantly reduce treatment costs while achieving both resource recovery and environmental benefits.
Supplier
Shanghai Lingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. was established in 2016 which is a professional manufacturer of biomagnetic materials and nucleic acid extraction reagents.
We have rich experience in nucleic acid extraction and purification, protein purification, cell separation, chemiluminescence, and other technical fields.
Our products are widely used in many fields, such as medical testing, genetic testing, university research, genetic breeding, and so on. We not only provide products but also can undertake OEM, ODM, and other needs. If you have a related need, please feel free to contact us .