Professional Manufacturer of Biomagnetic Beads

Exploring the Applicability of LnjnBio 22 Series Magnetic Bead Segmentation in Purification
Fragment Size Selection is a critical foundational step in molecular biology experiments such as DNA sequencing library preparation and cloning.
Its core purpose is to isolate DNA fragments within a specific size range from a mixture of fragments of varying lengths, enabling downstream applications.
Its principle primarily relies on the differences in physical, chemical, or electrical properties among DNA molecules of varying sizes, leveraging these distinctions to achieve separation and screening.
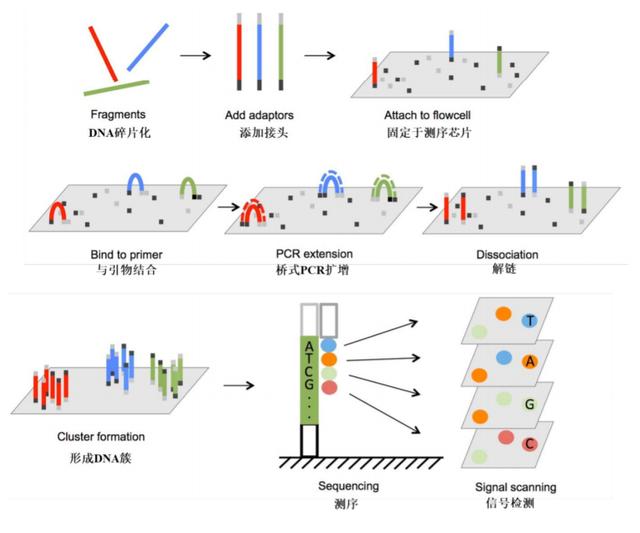
Magnetic bead purification (Solid-Phase Reversible Immobilization, SPRI) is currently the most widely used and efficient method, particularly in high-throughput sequencing (NGS) library preparation.
Principle:
Based on the relationship between DNA fragment size and magnetic bead binding efficiency.
Binding:
Add a specific concentration of polyethylene glycol (PEG) and salt (NaCl) to the DNA fragment solution, then introduce surface-modified magnetic beads. In a high-salt environment, DNA dehydrates and exposes its phosphate backbone, reversibly adsorbing to the bead surface via hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions. The key point is that larger DNA fragments bind more readily and earlier than smaller fragments.
Precipitation and Separation:
Place the reaction tube on a magnetic stand. Magnetic beads (along with bound DNA) will adhere to the tube wall, leaving unbound solution and small DNA fragments in the supernatant.
For large fragments:
Add a lower concentration of PEG/salt solution. Only large DNA fragments will bind to the magnetic beads. Discard the supernatant (containing unwanted short fragments), retain the magnetic beads, and elute the DNA to obtain long fragments.
For short fragments:
First add a medium-concentration PEG/salt solution to bind most DNA (including both long and short fragments) to the magnetic beads. Discard the supernatant, which will be completely devoid of DNA. Next, add a low-concentration PEG/buffer or water solution. Short DNA fragments will preferentially dissociate from the magnetic beads. Place the mixture back on the magnetic stand. Pipette off the supernatant containing the target small fragments, discarding the large fragments still bound to the beads.
Experimental Investigation:
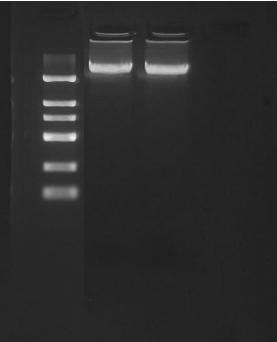
We selected foreign brand A magnetic beads (10 mg/ml) and our company’s R&D products: 220011 (50 mg/ml), 220012 (25 mg/ml), 220021 (50 mg/ml), and 220022 (25 mg/ml) (Table 1). Their solid content was standardized to 1.2 mg/ml under specific salt concentrations and PEG percentages. Following the purification steps for fragment selection, a first round of 0.6X purification was performed, followed by a second round of 0.2X purification on the supernatant from the first round. The results are shown in Figure 1.
Table 1: Magnetic beads selected for the fragment selection experiment
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Beads | A | 220011 | 220012 | 220021 | 220022 | 220022’ |
Note: 220022′ is another batch of magnetic beads

The results show that in the first round of 0.6X purification, the foreign A beads, 220011, 220021, 220022 and 220022′ were sorted above 500bp, while 220012 was sorted up to 400bp; from the second round of 0.2X separation, the foreign A beads, 220021, 220022 and 220022′ were mainly sorted 300-500bp, among which 220011 had a little residue due to the large fragment and needed to be further optimised, while 220012 needed to be further optimised due to the sensitivity of 220011 to pH. ‘s main sorting 300-500bp, of which 220011 has a little residue due to the large bands, probably due to 220011 is more sensitive to pH needs to be further optimised, while 220012 due to the first round of the recovery is higher can be appropriately adjusted the concentration of salt ions and PEG or adjust the sorting volume ratio to 0.55X + 0.2X to achieve the the same sorting effect.
From the above study, we can see that our 220011, 220012, 220021 and 220022 have great potential to replace foreign magnetic beads.
Magnetic bead purification has the advantages of high throughput, automation, rapidity and no toxic reagents (such as ethanol), so it can be widely used in NGS library purification, PCR product purification, cDNA sorting and so on.
We understand that the reproducibility of scientific research depends on the high stability of reagents. Each batch of magnetic beads undergoes strict quality control to ensure that the particles are uniform and the performance is stable, which ensures that you can obtain consistent and reliable results for every experiment. Our products are widely used in various molecular biology scenarios such as NGS library construction, digestion product purification, DNA fragment sorting, cDNA purification, etc. They are indispensable “all-rounders” in your laboratory.
Supplier
Shanghai Lingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. was established in 2016 which is a professional manufacturer of biomagnetic materials and nucleic acid extraction reagents.
We have rich experience in nucleic acid extraction and purification, protein purification, cell separation, chemiluminescence, and other technical fields.
Our products are widely used in many fields, such as medical testing, genetic testing, university research, genetic breeding, and so on. We not only provide products but also can undertake OEM, ODM, and other needs. If you have a related need, please feel free to contact us .