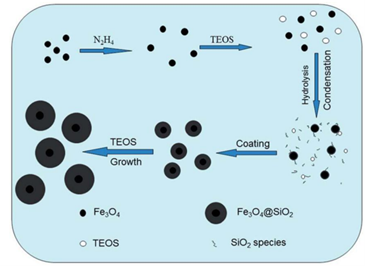
Professional Manufacturer of Biomagnetic Beads

How to improve the results of the 260/230 calculation using the magnetic bead method for extracting reagents?
When extracting nucleic acids using the magnetic bead method, a low 260/230 ratio (usually < 1.8) indicates the presence of organic compounds (such as guanidine salts, phenol, ethanol, EDTA) or residual salts in the sample, which can affect downstream experiments (such as PCR, sequencing).
Here is a systematic optimization plan:
- Optimization of Extraction Steps
a. Complete sample lysis
Problem: Incomplete lysis leads to incomplete release of impurities.
Improvement: Increase the lysis time (e.g., extend to 30 minutes) or temperature (56℃).
Add a grinding step or additional proteinase K digestion for complex samples (such as plants, feces).
b. Thoroughly wash the magnetic beads
Key step: Incomplete washing is the main cause of 260/230 low.
Improvement: Increase the number of washes: 2 times → 3 times (especially for samples with high impurities).
Washing solution formula: Ensure to use freshly prepared 80% ethanol (avoid excessive water content or contamination).
Washing operation: Vortex or shake to mix the magnetic beads each time, avoiding the formation of beads clumps.
Thoroughly aspirate the supernatant (can briefly centrifuge to remove residual liquid).
c. Complete drying of magnetic beads
Problem: Residual ethanol can significantly reduce 260/230.
Improvement: Open the cap and let it dry for 5-10 minutes (at room temperature or 37°C), until there is no ethanol smell. Avoid excessive drying (otherwise, it will reduce the efficiency of nucleic acid elution).
d. Optimize elution conditions
Use preheated elution buffer (such as 65°C TE buffer or sterile water), and let it stand for 5 minutes before collection.
Avoid using too small elution volume (recommend ≥ 50 μL to reduce salt concentration).
Ⅱ.Quality Control of Reagents and Consumables
a. Replace with fresh reagents:
Check if ethanol and washing solution have been contaminated (if stored for a long time without sealing).
Avoid using expired magnetic bead reagents (magnetic bead degradation may adsorb impurities).
b. Consumables selection:
Use centrifuge tubes and pipettes without nuclease or pyrogen (to avoid interference from plastic additives).
Ⅲ.Sample preprocessing
- Complex samples (such as soil and plants):
Increase the CTAB or SDS pretreatment to remove polysaccharides and polyphenols.
- For blood samples:
First remove hemoglobin using erythrocyte lysis solution.
- Inhibitor-enriched samples (such as feces and body fluids):
Dilute the samples or use dedicated lysis buffers (such as those containing Carrier RNA).
Ⅳ.Verification and remedial measures
a. Electrophoresis or Qubit verification:
Check for degradation (tailing phenomenon) using agarose gel electrophoresis.
Compare the results with those from Nanodrop using a fluorescence meter (Qubit) to eliminate interference from impurity absorbance.
b. Purification remediation:
If the ratio of 260/230 remains low, purify the nucleic acid using a silica column or by ethanol precipitation again.
V. Control Experiment
For each extraction, a known standard sample (such as λDNA or cultured cells) is set up to confirm the stability of the reagents.
If the 260/230 ratio of the control sample is normal, the problem may lie in the sample being tested itself.
Common Problem Troubleshooting Checklist
| Phenomenon | Possible Cause | Solution |
| 260/230 is low but 260/280 is normal | Protein or phenol contamination | Strengthen the washing and drying steps |
| Both 260/230 and 260/280 are low | Protein or phenol contamination | Optimize the lysis, replace the lysis solution |
| Only the 230 peak is high | Organic solvent contamination | Check the purity of ethanol or buffer |
By following these steps, the ratio of 260/230 can be significantly increased (target > 1.8). If the problem persists, please feel free to contact Shanghai Lingjun Biotechnology at 18103799069.
Supplier
Shanghai Lingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. was established in 2016 which is a professional manufacturer of biomagnetic materials and nucleic acid extraction reagents.
We have rich experience in nucleic acid extraction and purification, protein purification, cell separation, chemiluminescence, and other technical fields.
Our products are widely used in many fields, such as medical testing, genetic testing, university research, genetic breeding, and so on. We not only provide products but also can undertake OEM, ODM, and other needs. If you have a related need, please feel free to contact us .