Professional Manufacturer of Biomagnetic Beads

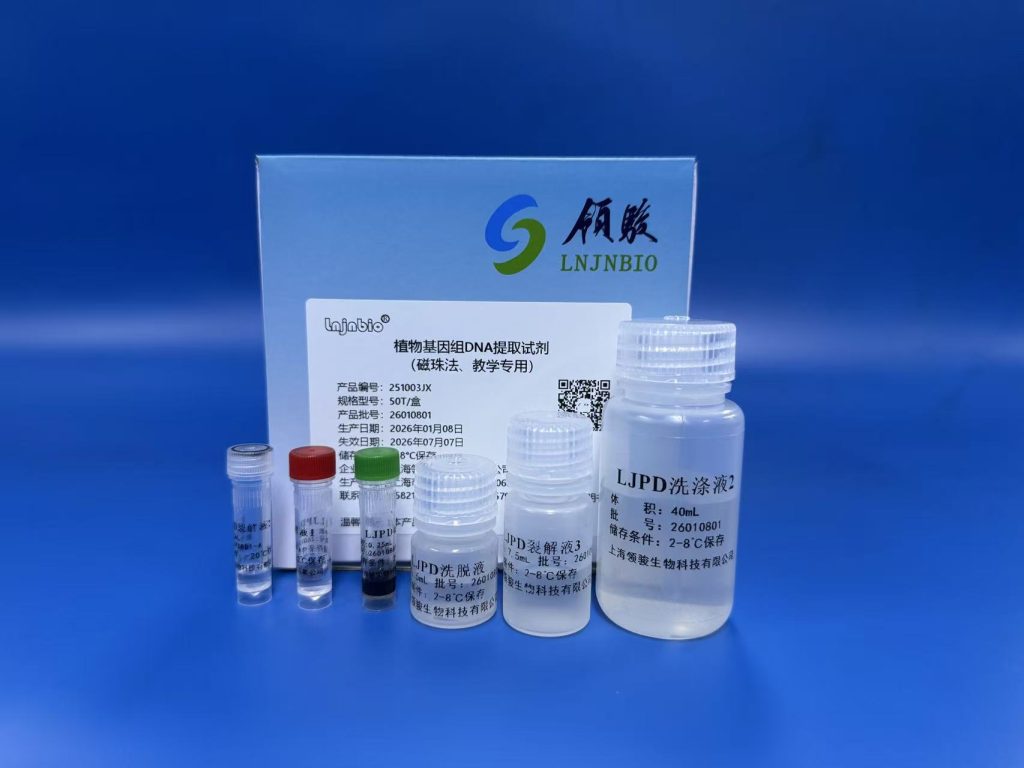
Plant Genomic DNA Extraction Kit (Magnetic Bead Method, Educational Use Only)
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
- Product No.:251003JX
- Extraction Methods: magnetic bead method
- Sepc: Bottled:50 T/box、100 T/ box、200 T/ box
Description
【Product Introduction】
The sample releases nucleic acids under the action of the lysis buffer. Magnetic beads selectively adsorb the nucleic acids in the binding buffer, separating them from other impurities in the sample. Subsequently, the mixture is washed with a washing buffer to remove proteins, polysaccharides, inorganic salt ions, and other contaminants. Finally, high-quality DNA is obtained through elution.
【Product advantages】
- Streamlined procedure with flexible timing to accommodate laboratory session schedules (typically 30–60 minutes)
- Replacement of DTT with a reducing agent free from highly toxic organic solvents such as phenol and chloroform, and without pungent odours
- Eliminates the need for repeated centrifugation, ensuring high-purity, high-yield DNA products with intact electrophoresis bands
- Facilitates the cultivation of scientific thinking and standardised procedures among students, broadening their scientific horizons
- Suitable for extracting genomic DNA from the tender leaves and seeds of various plants (such as Chinese spinach, spinach, Shanghai green, Chinese cabbage, lettuce, coriander, wheat, rice, maize, soybeans, etc.) for subsequent PCR amplification and detection.
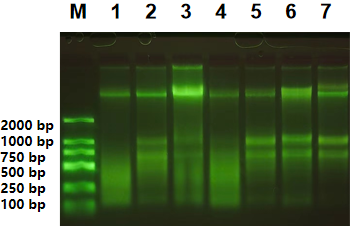
【Experimental Case】
Genomic DNA extraction experiments were conducted using 5mg samples of various fresh, young tissues, yielding the following results:
| No. | Sample | A260/A280 | A260/A230 | Conc. (ng/μL) |
| 1 | Pak choi | 1.956 | 2.035 | 359.9 |
| 2 | Onion | 1.922 | 2.108 | 305.9 |
| 3 | Spinach | 1.95 | 1.894 | 495.85 |
| 4 | Bok choy | 1.979 | 2.069 | 658.7 |
| 5 | Chinese cabbage | 1.924 | 1.973 | 318.8 |
| 6 | Coriander | 1.975 | 2.152 | 756.3 |
| 7 | Lettuce | 1.896 | 1.84 | 122.55 |
【Application area】
The nucleic acids extracted and purified using this kit may be employed in a variety of downstream molecular biology experiments, including PCR, quantitative real-time PCR, digital PCR, restriction enzyme digestion, Southern blotting, SNP genotyping, next-generation sequencing, and library preparation.
FAQs
We have magnetic beads in silica, magnetic beads in carboxylic acid, and various kits for nucleic acid extraction by magnetic bead method (samples can be extracted from whole blood, serum plasma free, plasmid, etc.), and the packing specifications of magnetic beads are 2ml, 10ml, 50ml, 500ml, 1000ml, etc. The packing specifications of the kits are: bottles are 50T/box, 100T/box, 200T/box, and the pre-filled kits are 32T/box, 48T/box, 64T/box, 96T/box, and 48T/box. We have 32T/box, 48T/box, 64T/box, 96T/box, and so on.
Land transportation, sea transportation, air transportation, you can choose according to your requirements.
Of course, we provide customized service and also support OEM\ODM.
First, confirm the demand, then sign the contract; after receiving the payment, we will ship the goods within the stipulated or mutually agreed delivery period.
Usually, we will send out the goods within 15 working days after receiving the payment; customized products and large quantities of orders (magnetic beads ≥ 10L, nucleic acid extraction reagents ≥ 300000T) need to be determined by both sides to communicate with the delivery period.
REQUEST A QUOTE
-
WeChat: +86 193 7079 1286