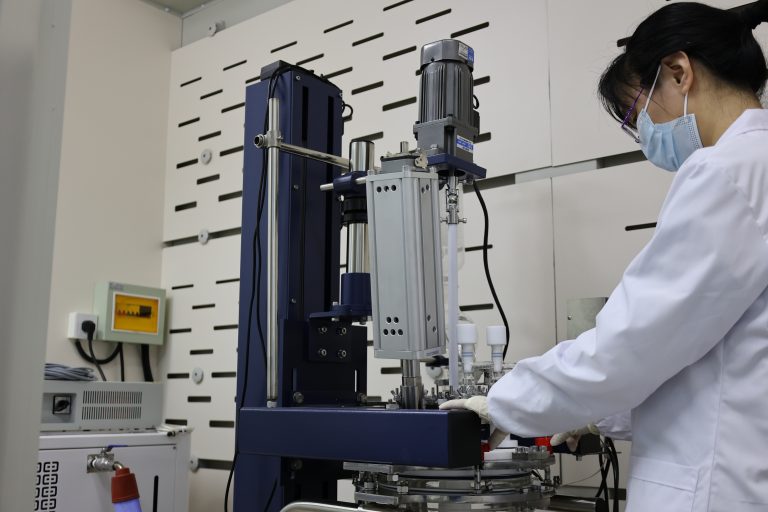
Professional Manufacturer of Biomagnetic Beads

Magnetic Bead-Based Nucleic Acid Extraction Instruments in NGS Library Preparation
Magnetic bead-based nucleic acid extraction instruments play a critical and almost indispensable role in the next-generation sequencing (NGS) library preparation workflow. As the starting point of the entire NGS process, their performance directly determines the quality of subsequent library construction and sequencing data.
Below are the core applications and advantages of magnetic bead-based nucleic acid extraction instruments in NGS library prep:
Core Task: Isolation and Purification of High-Quality Nucleic Acids
Diverse Starting Samples: NGS library prep begins with an extremely wide range of sample types, including blood, plasma (cell-free DNA), saliva, tissue (fresh/FFPE), cells, microorganisms, plants, and environmental samples. Magnetic bead methods, due to their flexibility and optimizability, can handle these complex samples, which often contain significant amounts of inhibitors.
Target Nucleic Acid Types: Primarily used to extract DNA (genomic DNA, gDNA; cell-free DNA, cfDNA) or RNA (for RNA-Seq). Functional groups coated on the magnetic bead surface (typically silanol groups or specific ion-exchange groups/affinity ligands) selectively bind nucleic acids under specific buffer conditions.
Impurity Removal: Efficiently removes proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, salt ions, detergents, humic acids (environmental samples), fixatives and dyes (FFPE samples), and PCR inhibitors (e.g., heparin, heme, humic acids) from samples. These impurities can severely interfere with subsequent enzymatic reactions (e.g., fragmentation, end repair, dA-tailing, adapter ligation, PCR amplification), leading to library prep failure, reduced efficiency, or poor sequencing data quality.
Key Roles in the NGS Library Prep Workflow
Providing Pure “Raw Material” for Library Prep: Library preparation steps (fragmentation, end repair/dA-tailing, adapter ligation, PCR amplification) all require high-purity nucleic acids of suitable integrity and sufficient concentration as input. Magnetic bead extraction is the critical step ensuring qualified “raw material.”
Ensuring Library Representativeness and Uniformity: Efficient and uniform nucleic acid recovery is vital for maintaining the true proportion of nucleic acid molecules in the original sample, especially when studying low-frequency variants, metagenomics, or transcriptomics. The high recovery rate and consistency of magnetic bead methods help minimize bias.
Improving Library Prep Success Rate and Efficiency: By removing inhibitors, the expensive enzymes used in library prep (e.g., polymerases, ligases) can function more effectively, reducing the risk of enzyme inactivation or incomplete reactions, thereby increasing library yield and quality.
Meeting Low-Input Sample Requirements: For precious, low-quantity samples like cfDNA, single-cell sequencing samples, or needle biopsies, magnetic bead methods, due to their high binding efficiency and recovery rate (especially with optimized kits), can obtain sufficient nucleic acids for library prep from minimal starting material.
Handling Challenging Samples: Specially optimized magnetic bead kits and protocols exist for challenging samples like FFPE (containing cross-linked and fragmented DNA, plus high levels of fixatives/dyes), soil/environmental samples (containing complex inhibitors), and polysaccharide/polyphenol-rich plant samples, enabling effective cell/tissue lysis and purification of usable nucleic acids.
Core Advantages of Magnetic Bead Nucleic Acid Extraction Instruments (Why They Are Preferred for NGS)
Automation & High Throughput:
Core Advantage: Instruments can process multiple samples simultaneously (from a few to 96/384-well plates), enabling standardized operations. This is crucial for NGS projects requiring large sample volumes (e.g., population studies, clinical testing), significantly increasing throughput and efficiency.
Reduced Human Error: Automation minimizes variability and contamination risks from manual handling, improving result consistency and reproducibility.
Simple and Rapid Operation: Compared to traditional phenol-chloroform or spin-column methods, magnetic bead methods on automated instruments involve fewer steps (lysis-bind-wash-elute), offer a simpler workflow, and drastically reduce extraction time (typically 30-60 minutes per batch).
High Purity and Yield: Optimized magnetic bead surface chemistry and buffer systems enable efficient, specific nucleic acid binding and washing, effectively removing impurities to obtain high-purity, high-concentration nucleic acids that meet NGS’s stringent input quality requirements (e.g., A260/A280, A260/A230 ratios, concentration, fragment size distribution).
Flexibility: By switching different magnetic beads and kits, the same instrument can adapt to various sample types (blood, tissue, cells, FFPE, microbes, etc.) and nucleic acid types (DNA, RNA, total nucleic acid), and can even integrate DNase digestion steps.
Closed System & Low Contamination Risk: Automated instruments typically handle liquids in a relatively closed or semi-closed environment. Combined with magnetic bead capture (no columns or repeated centrifugation/open caps), this significantly reduces the risk of cross-contamination between samples and aerosol contamination.
Scalability: Instruments with different throughput capacities (e.g., 8, 16, 32, 96 wells) can be selected based on lab needs.
Safety: Avoids the use of toxic organic solvents like phenol-chloroform, making it safer and more environmentally friendly.
Easy Integration: Modern automated workstations can integrate magnetic bead nucleic acid extraction with subsequent library prep steps (e.g., fragmentation, enzymatic treatments, purification) and even quantification, enabling fully automated “sample-in, library-out” workflows.
Application Scenario Examples
Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS): Extraction of high-quality gDNA from blood, saliva, or tissue.
Whole Exome Sequencing (WES): Also requires high-quality gDNA as starting material.
Targeted Sequencing: Extraction of nucleic acids from various samples for sequencing specific gene regions.
RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq): Extraction of high-quality total RNA or mRNA for transcriptome analysis.
Metagenomic Sequencing: Extraction of total microbial community DNA from environmental samples (soil, water, gut contents) or clinical samples (respiratory swabs).
Cell-Free DNA (cfDNA) Sequencing: Extraction of trace cfDNA from plasma or serum for non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) or liquid biopsy for cancer.
Single-Cell Sequencing: Extraction of minute amounts of genomic DNA or RNA from lysed single cells.
FFPE Sample Sequencing: Extraction of fragmented DNA from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues for retrospective studies or clinical diagnostics.
Selection and Usage Considerations
Kit Matching: Must select magnetic bead kits optimized for the specific sample type and nucleic acid type.
Instrument Performance: Consider instrument throughput, magnet adsorption efficiency, liquid handling precision, cross-contamination control, run time, etc.
Bead Quality: Bead size uniformity, magnetic strength, surface coating stability, and nucleic acid binding capacity are crucial.
Lysis Efficiency: For complex samples (e.g., tissue, Gram-positive bacteria, spores), efficient lysis is a prerequisite for successful extraction and may require optimized lysis conditions or special lysis modules.
Elution Volume: Smaller elution volumes help achieve high nucleic acid concentrations but require ensuring complete dissolution without loss.
Residual Inhibitors: Even with magnetic bead methods, trace inhibitors may remain in certain samples (e.g., stool, soil, FFPE), requiring extra caution or dilution in subsequent library PCR steps.
Summary:
Magnetic bead-based nucleic acid extraction instruments, with their automation, high throughput, speed, efficiency, high purity, simplicity of operation, safety, and flexibility, have become the predominant nucleic acid purification technology in NGS library preparation workflows. They provide the pure, reliable, and uniform nucleic acid “raw material” essential for high-quality NGS library construction, serving as the cornerstone for successful NGS workflows and reliable sequencing data. Whether for basic research or clinical diagnostics, automated magnetic bead nucleic acid extraction is an indispensable key step.
Supplier
Shanghai Lingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. was established in 2016 which is a professional manufacturer of biomagnetic materials and nucleic acid extraction reagents.
We have rich experience in nucleic acid extraction and purification, protein purification, cell separation, chemiluminescence, and other technical fields.
Our products are widely used in many fields, such as medical testing, genetic testing, university research, genetic breeding, and so on. We not only provide products but also can undertake OEM, ODM, and other needs. If you have a related need, please feel free to contact us .