Professional Manufacturer of Biomagnetic Beads

News
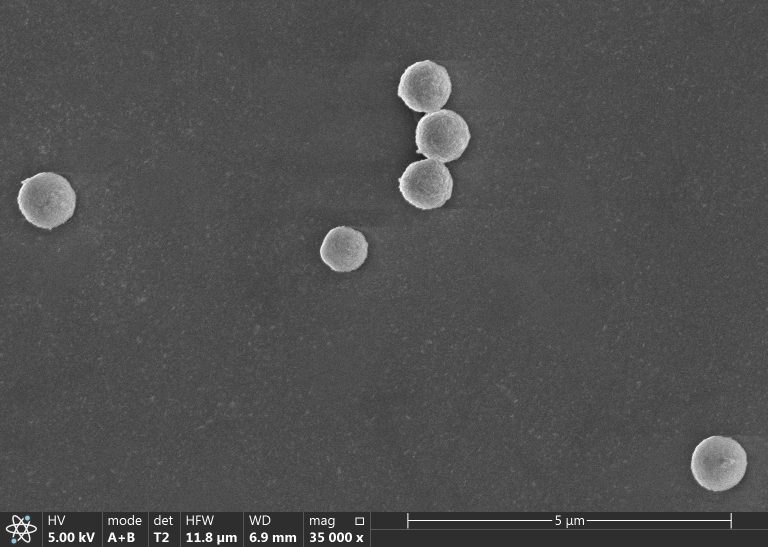

Exploring the Applicability of LnjnBio 22 Series Magnetic Bead Segmentation in Purification
Fragment Size Selection is a critical foundational step in molecular biology experiments such as DNA sequencing library preparation and cloning. Its core purpose is to isolate DNA fragments within a specific size…

How significantly does temperature affect silica hydroxyl and carboxyl magnetic beads?
The effect of temperature on silica hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxyl (-COOH) magnetic beads is very significant, primarily impacting stability, binding capacity, and aggregation tendency. The specific effects vary depending on the bead…
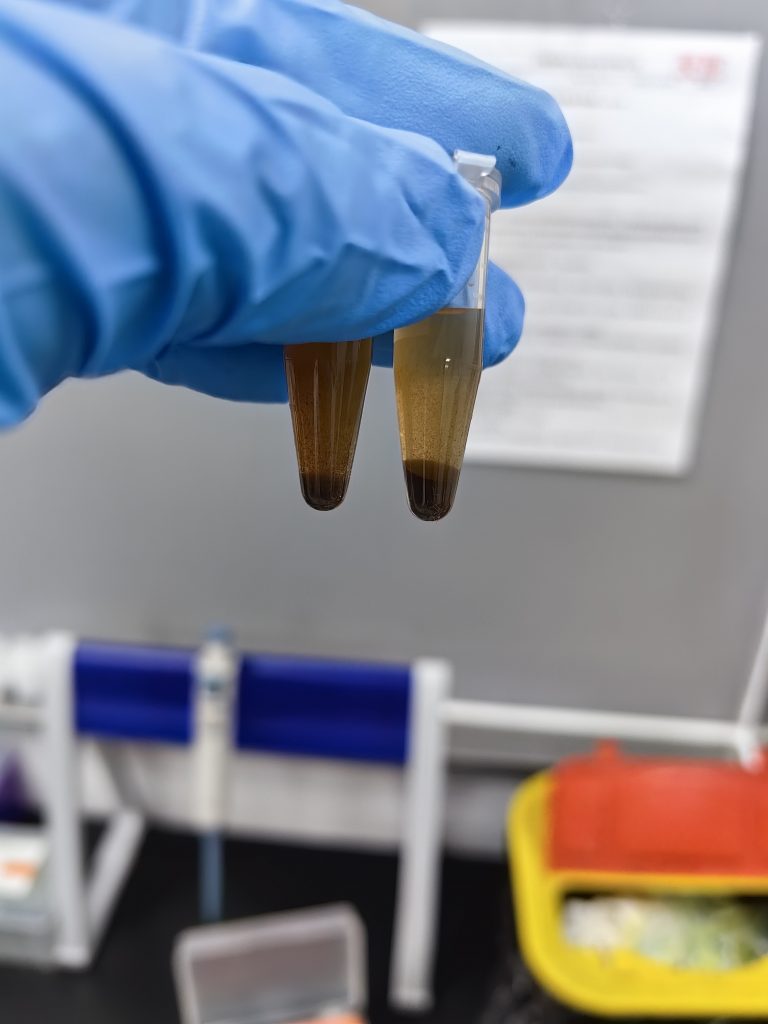
LnjnBio 160014 Magnetic Beads,Unleashing the Limitless Potential of Life Science Research
LnjnBio 160014 magnetic beads feature a superparamagnetic Fe3O4 core-SiO2shell structure. Through precise control of the silanization modification process, a high-density hydroxyl functional group is constructed on the bead surface. This unique structure enables…

Revolutionize ASF Testing with Magnetic Bead Extraction Technology
Dear valued customer, we heard you’re locked in a battle of wits with the African swine fever virus? Don’t worry—we’ve got the “Magnetic Fishing Rod” (Lingjun 160011 Magnetic Beads), specially designed to…

Lnjnbio 160024 Magnetic Beads: Extracting New ‘Beads’
In today’s bioscience research and medical diagnostic field, the purity and efficiency of nucleic acid extraction directly affect the accuracy and reliability of experimental results. The 160024 DNA/RNA Nucleic Acid Extraction Beads…

Why are more and more college teachers using the magnetic bead method instead of the traditional one?
In recent years, magnetic bead-based nucleic acid extraction technology has been rapidly popularized in universities and research institutions, gradually replacing the traditional phenol-chloroform extraction and centrifugal column methods. This is mainly attributed…

Revolutionary nucleic acid extraction technology: Shanghai Lingjun Bio 220011 magnetic beads lead a new era of scientific research efficiency
The progress of scientific research often begins with small innovations in experimental tools. In countless laboratories, a silent technological revolution is taking place. In the fields of genomics, molecular diagnostics, and biomedical…
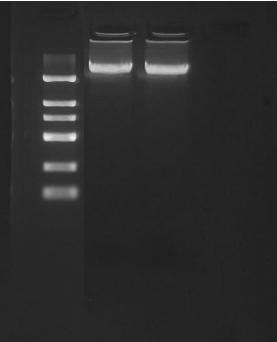
Magnetic Beads for Plasmid DNA Extraction and Purification 160024: Double Guarantee for Experimental Efficiency and Quality
Are you still wasting energy on inefficient plasmid DNA extraction processes? The 160024 silica-based magnetic beads can significantly improve extraction efficiency and purity. Covering all scenarios from scientific research to quality inspection,…

Shanghai LNJNBio nucleic acid extraction program is escorting the detection of African swine fever
At a time when the prevention and control of African swine fever (ASF) remains a serious challenge, rapid and accurate laboratory testing serves as the first line of defense for early detection…
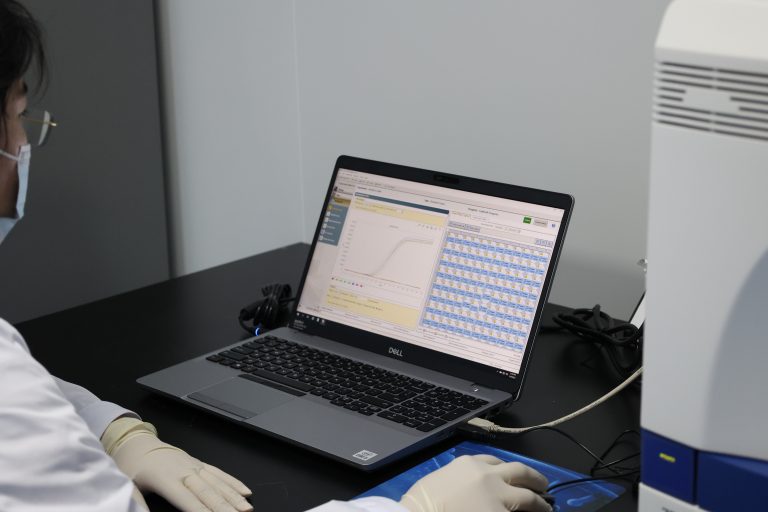
Effortless Extraction of High-Quality DNA – Magnetic Bead Blood Genomic DNA Extraction Kits Accelerate Research!
In fields such as molecular biology, genetics, and clinical diagnostics, the extraction of high-quality genomic DNA is a critical step for experimental success. Traditional DNA extraction methods are often cumbersome, time-consuming, and…
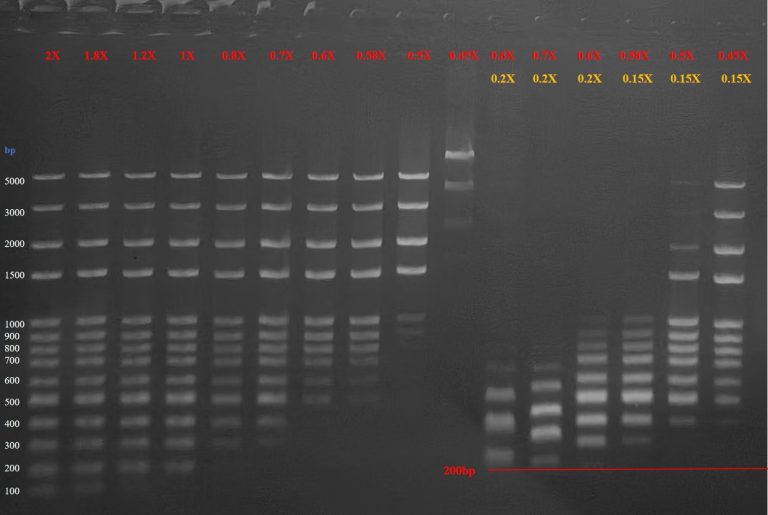
Precise capture, efficient purification —— Shanghai LNJNBio 220012 magnetic beads help scientific research take off
In molecular diagnostics, nucleic acid extraction, and immunoassays, high-efficiency magnetic bead separation technology has become essential for successful experiments. Shanghai Lingjun Biotech’s 220012 magnetic beads, with their exceptional superparamagnetic properties, high binding…
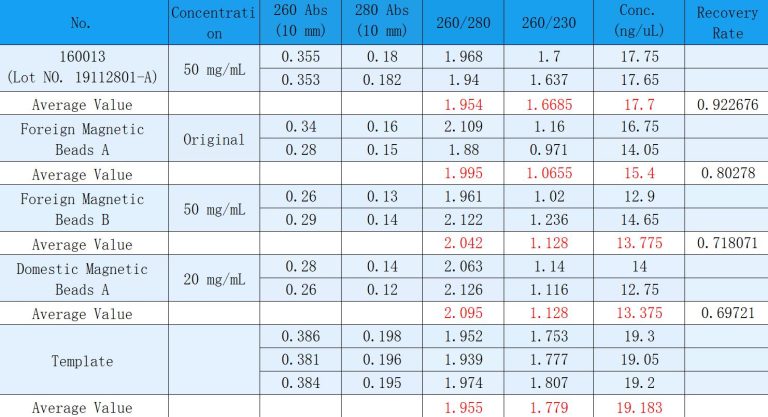
160013 Magnetic Beads: The “Golden Partner” for Nucleic Acid Extraction with Guaranteed High Recovery Rate
Still looking for a reliable helper for DNA/RNA extraction and purification? The Viral DNA/RNA Extraction and Purification Magnetic Beads – 160013 from Shanghai Lingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. can be called the “golden…
