Professional Manufacturer of Biomagnetic Beads

Nucleic acid aptamers: a new dawn for tumor detection
Introduction
In the field of cancer detection, emerging technologies are creating new opportunities to enhance diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. Nucleic acid aptamers are gaining prominence as a groundbreaking approach. These single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules, selected through in vitro screening, fold into unique three-dimensional structures that bind with high affinity to specific targets. Compared to traditional antibodies, they demonstrate significant advantages including high design flexibility, easy modification, enhanced biosafety, and improved stability, showcasing tremendous potential for cancer detection applications.
1. Nucleic acid aptamer technology has demonstrated remarkable performance in early tumor diagnosis.
Traditional detection methods face limitations in identifying early-stage tumors, whereas nucleic acid aptamers can precisely recognize and bind to specific biomarkers on tumor cell surfaces, such as particular proteins or receptors. For instance, the multivalent nucleic acid aptamer nanocarrier (pAPNC) developed through collaboration between Hefei University of Technology and Hunan University consists of a multivalent nucleic acid aptamer shell and a protein core. This system exhibits high affinity for receptor proteins overexpressed on cancer cells, demonstrates strong stability in serum, and exhibits excellent nuclease resistance, enabling effective drug loading. It shows great promise for early tumor imaging diagnosis. By constructing nucleic acid aptamer-based sensors—such as electrochemical, fluorescence, and colorimetric sensors—precise detection of tumor-associated exosomes can be achieved. Exosomes, as microvesicles secreted by cells, carry various biological information from tumor cells. Their detection aids in early diagnosis. Electrochemical sensors can quantify exosomes through electrical signal changes induced by aptamer-binding, achieving a detection limit as low as 10³ cells/mL. This enables rapid analysis of blood samples, providing an efficient method for early tumor screening.
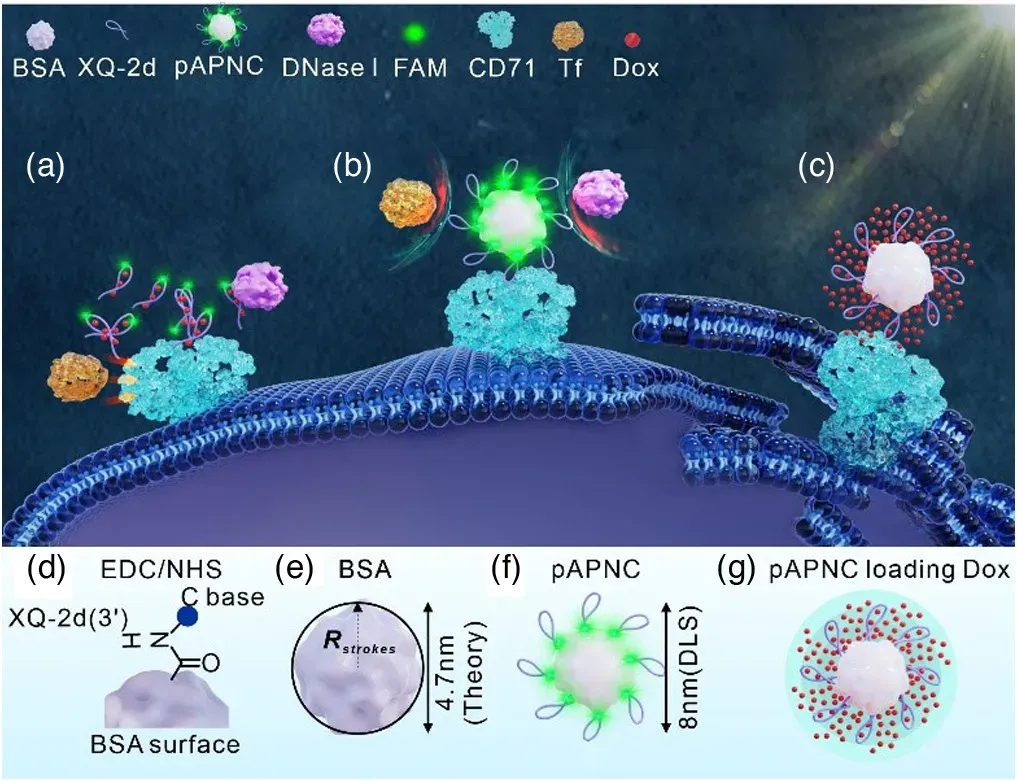
Figure 1. pAPNC has high affinity, high receptor accessibility, high nuclease resistance and high drug loading capacity
2. Nucleic acid aptamers have demonstrated remarkable potential in precision tumor classification and personalized treatment.
Given the distinct molecular characteristics of different cancer cell types, these aptamers enable the targeted synthesis of probes for specific malignancies such as leukemia, lung cancer, and breast cancer. The research team led by Academician Tan Weihong has developed nucleic acid aptamer probes conjugated with radioactive isotopes. When administered to patients, these probes utilize PET imaging technology to effectively identify tumor cells while precisely distinguishing between inflammatory responses and malignant growths. This breakthrough allows clinicians to formulate more targeted treatment plans, thereby avoiding unnecessary surgical interventions and excessive medication regimens.
3. Furthermore, nucleic acid aptamers play a vital role in tumor treatment monitoring.
By continuously tracking the binding between tumor cell surface markers and aptamers, clinicians can assess treatment efficacy and adjust therapeutic strategies promptly. When treatment proves effective, changes in tumor cell surface marker expression may occur, leading to corresponding alterations in aptamer binding signals. This provides doctors with clear indicators to monitor treatment progress, offering a tangible basis for clinical decision-making.
Summary
While nucleic acid aptamer technology shows great promise in cancer detection, it currently faces challenges such as heterogeneity interference from exosomes, insufficient stability in vivo, and the need to enhance resistance against complex matrices. However, with the continuous advancement of cutting-edge technologies like high-throughput sequencing, computer-aided design, and multi-technology integration, this technology is expected to be further optimized. It will gradually transition from laboratory research to routine clinical testing, bringing more benefits to cancer patients and helping elevate the diagnostic and therapeutic standards of oncology to new heights.
Supplier
Shanghai Lingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. was established in 2016 which is a professional manufacturer of biomagnetic materials and nucleic acid extraction reagents.
We have rich experience in nucleic acid extraction and purification, protein purification, cell separation, chemiluminescence, and other technical fields.
Our products are widely used in many fields, such as medical testing, genetic testing, university research, genetic breeding, and so on. We not only provide products but also can undertake OEM, ODM, and other needs. If you have a related need, please feel free to contact us .