Professional Manufacturer of Biomagnetic Beads

Simplifying Blood DNA/RNA Extraction with Silica-Based Magnetic Beads
1.Introduction
Silica-based magnetic beads, used in nucleic acid extraction, represent a core and mature technology in modern molecular biology, medical diagnostics, and genetic testing. Their fundamental principle involves using surface-modified magnetic nanoparticles (magnetic beads) that specifically bind to nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) via electrostatic interactions and hydrophobic forces under specific buffer conditions, enabling the separation and purification of nucleic acids through the application of an external magnetic field.

2. Core Principle: Why Do silica-based magnetic beads Adsorb Nucleic Acids?
The core of silica-based magnetic beads is made of magnetic materials such as iron oxide (Fe₃O₄), coated with a layer of silica (SiO₂). Under specific conditions, the silica surface can bind to nucleic acids, primarily through hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonding under high-salt and low-pH conditions.
2.1 Lysis and Binding:
Under the action of a lysis buffer (typically containing high concentrations of chaotropic salts like guanidine hydrochloride or guanidine isothiocyanate) and detergents, the cell membranes and nuclear membranes in the blood are disrupted, releasing nucleic acids.
Simultaneously, high concentrations of chaotropic salts disrupt the hydrogen bonding structure between water molecules, forming a “salt bridge” around the nucleic acids and magnetic beads. This neutralizes the negative charge of the nucleic acid phosphate backbone, eliminating electrostatic repulsion between nucleic acid molecules.
This transforms the originally hydrophilic nucleic acids into a hydrophobic state, allowing them to efficiently adsorb onto the hydrophobic surface of the silica-based magnetic beads via hydrophobic interactions.
2.2 Washing:
Under the influence of a magnetic field, the magnetic beads bound with nucleic acids are attracted to the tube wall, and the supernatant (containing impurities such as proteins, heme, lipids, and salt ions) is discarded.
A 70%-80% ethanol wash solution is added. Ethanol maintains the binding between the nucleic acids and the magnetic beads while effectively dissolving and washing away hydrophilic impurities such as proteins and salts. The hydrophobic nucleic acid-magnetic bead complexes remain bound.
2.3 Elution:
After discarding the ethanol wash solution and allowing it to dry, a low-salt or salt-free elution buffer (such as TE buffer or sterile water) is added.
The low ionic strength environment disrupts the “salt bridge,” allowing water molecules to rehydrate the nucleic acids, restoring their hydrophilicity and negative charge. This causes the nucleic acids to detach from the hydrophobic surface of the magnetic beads and dissolve into the elution buffer.
Finally, under the influence of a magnetic field, the elution buffer containing pure nucleic acids is transferred to a new tube, completing the extraction.
3. Advantages in Blood Nucleic Acid Extraction
Compared to traditional phenol-chloroform extraction and centrifugal column methods, the silica magnetic bead method offers significant advantages for processing whole blood samples:
- Automation and High Throughput: The entire process can easily be adapted to formats such as 96-well plates, making it highly suitable for automation using liquid handling workstations. This greatly increases sample throughput, meeting the demands of large-scale clinical testing.
- Simple and Fast Operation: Eliminates the need for multiple centrifugation steps and cumbersome liquid transfers, reducing manual operations and processing time. The entire procedure is typically completed within 20-40 minutes.
- High Safety: Avoids the use of toxic reagents such as phenol and chloroform, making it safer for operators and the environment.
- High Extraction Quality: Effectively removes high-abundance inhibitors in blood, such as heme, immunoglobulins, and lactoferrin. The resulting nucleic acids are of high purity and integrity, making them ideal for downstream applications like PCR, qPCR, and sequencing.
- Flexibility: The amounts of magnetic beads and reagents can be flexibly adjusted based on the starting sample volume (from a few microliters to several milliliters).
- High Recovery Rate: Offers better efficiency in recovering low-concentration nucleic acids compared to centrifugal column methods.
4. Specific Applications
Silica magnetic bead blood nucleic acid extraction technology is widely used in:
Infectious Disease Diagnostics: Viral load testing for pathogens such as HIV, HBV, HCV, and SARS-CoV-2.
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT): Extracting fetal cell-free DNA from maternal peripheral blood for genetic disease screening.
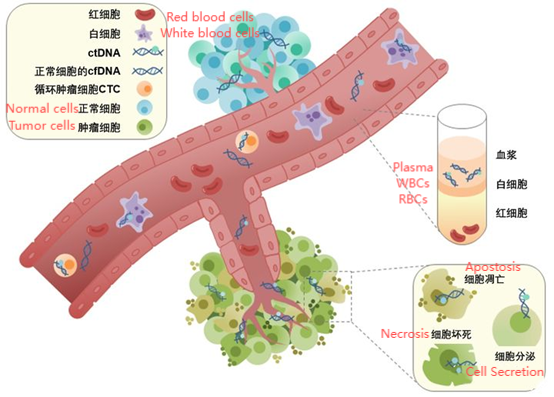
Circulating Tumor DNA (ctDNA) Detection: Used for early cancer screening, treatment efficacy monitoring, and prognosis assessment.
Forensics: Extracting DNA from bloodstains and other crime scene evidence for STR profiling and personal identification.
Blood Bank Screening: Nucleic acid screening of donor blood for pathogens.
Genetic Disease Research: Extracting gDNA from blood samples for genetic mutation analysis.
5. Application Case of Shanghai Lingjun silica-based magnetic beads Product 160014 in Blood Nucleic Acid Extraction
Using Lingjun Bio’s 160014 silica-based magnetic beads alongside Lingjun’s Blood Genomic DNA Extraction Kit on the LJbio-32H automated nucleic acid extraction and purification system, genomic DNA was extracted from four blood samples.
The experimental results are shown in the figure below:
| Sample | number | 260/280 | 260/230 | Conc. (ng/ul) | Nucleic acid yield(μg) |
| Blood sample 1200ul | 1 | 1.809 | 1.933 | 91.35 | 9.1 |
| 2 | 1.804 | 1.931 | 84.9 | 8.5 | |
| avg | 1.8065 | 1.932 | 88.13 | 8.8 | |
| Blood sample 2200ul | 3 | 1.794 | 2.053 | 106.95 | 10.7 |
| 4 | 1.788 | 2.003 | 93.6 | 9.4 | |
| avg | 1.791 | 2.028 | 100.28 | 10 | |
| Blood sample 3200ul | 5 | 1.802 | 2.026 | 97.5 | 9.8 |
| 6 | 1.793 | 2.019 | 112.7 | 11.3 | |
| avg | 1.7975 | 2.0225 | 105.1 | 10.5 |
Agarose gel electrophoresis:
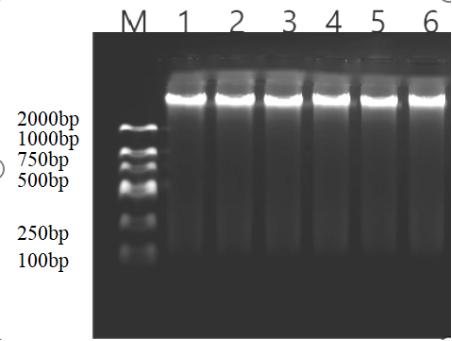
Analysis of Results:
Genomic DNA was stably extracted from all three samples,the 260/280 ratios were all above 1.79, and the 260/230 ratios were all above 1.9.
The yield from 200 μL samples was above 8 μg, sufficient for downstream applications,and The electrophoresis bands were intact, with no degradation or smearing.
6.Conclusion
The silica magnetic bead method has become the gold standard technology for nucleic acid extraction from whole blood/blood samples. It perfectly balances efficiency, quality, throughput, and automation, providing robust support for modern molecular diagnostics and life science research. Its physicochemical principle of “high-salt binding, low-salt elution” is simple yet highly efficient. Through continuous process optimization and reagent formulation improvements, it meets the demands of various complex samples and stringent downstream applications.
The development of precision medicine and personalized diagnostics requires higher sensitivity, speed, and automation in blood nucleic acid extraction. Silica magnetic bead technology will continue to be the core driver of innovation and advancement in this field.
Supplier
Shanghai Lingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. was established in 2016 which is a professional manufacturer of biomagnetic materials and nucleic acid extraction reagents.
We have rich experience in nucleic acid extraction and purification, protein purification, cell separation, chemiluminescence, and other technical fields.
Our products are widely used in many fields, such as medical testing, genetic testing, university research, genetic breeding, and so on. We not only provide products but also can undertake OEM, ODM, and other needs. If you have a related need, please feel free to contact us .